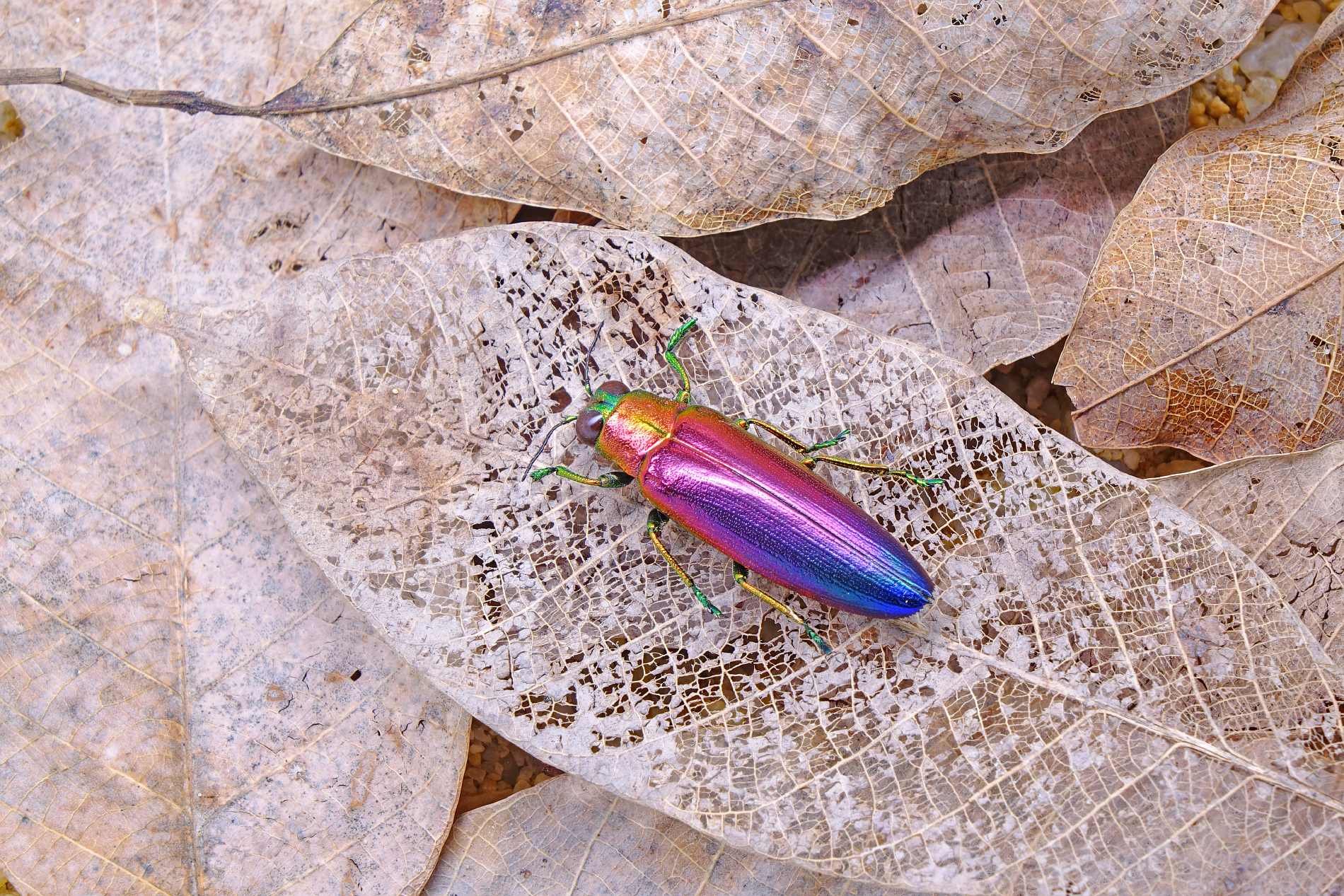
The jewel beetle has a shiny, brilliant color on its chitinous shell called the carapace. Buprestidae is their scientific name, but they are known as jewel beetles or metallic wood-boring beetles. The larvae are known as flat-headed borers. There are 15,500 species known in 775 genera. Insect collectors are very passionate about some of the most vibrantly colored large beetles in this species. In many countries like Japan, Thailand, and India, the colorful shells are used for making beetle wing jewelry. These bugs are mostly cylindrical, elongated, or ovoid in shape. They also come with interesting and complicated patterns along with their brilliant colors. The bright colors of the jewel beetle are not because of the pigments in the exoskeleton but it is caused by structural coloration in which the microscopic texture of their cuticle selectively reflects specific frequencies of light in a particular direction. These include the inaba jewel beetle, green jewel beetle, new leaf jewel beetle, golden jewel beetle, rainbow jewel beetle, purple jewel beetle, emerald jewel beetle, and more.
Some of these jewel beetles, also known as metallic-wood borer beetles, come under the serious pest category due to their capabilities to cause serious damage on a large scale. One such pest jewel beetle is the emerald ash borer. They can see infrared light from a distance which helps them to get closer to a forest fire. They come in colors like reds, greens, blues, and purples. Jewel beetles are known to thrive on deadwood. They lay their eggs there and develop their various larvae stages inside the deadwood.
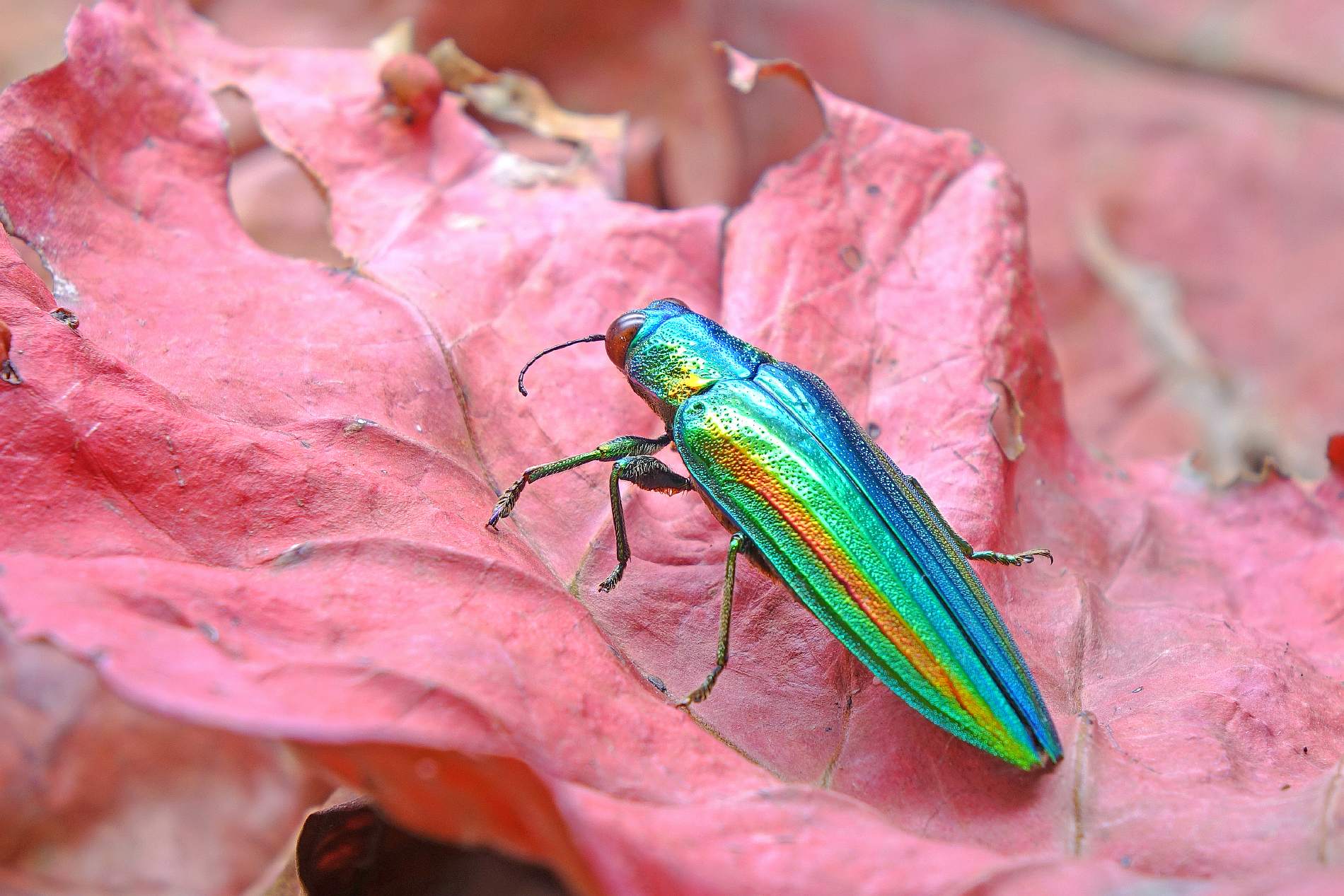

What type of animal is a jewel beetle?
The jewel beetle is a type of beetle species or a bug found in the forest trees in the northern hemisphere. They are famous for their vividly colored bodies in jewel or metallic colors. Some of the subspecies include Japanese jewel beetle, giant jewel beetle, African jewel beetle, Australian jewel beetle, and more.
What class of animal does a jewel beetle belong to?
The jewel beetle belongs to the insect class of animals, family Buprestidae. They are brilliantly colored insects whose species are known as pests, too, which cause great economic damage to farmlands and gardens. These insects are widely found in forest trees.
How many jewel beetles are there in the world?
The exact number of jewel beetles across the world would be difficult to calculate as they are difficult to calculate. There are hundreds of subspecies and genera for this species which makes it all the more difficult to come up with exact numbers.
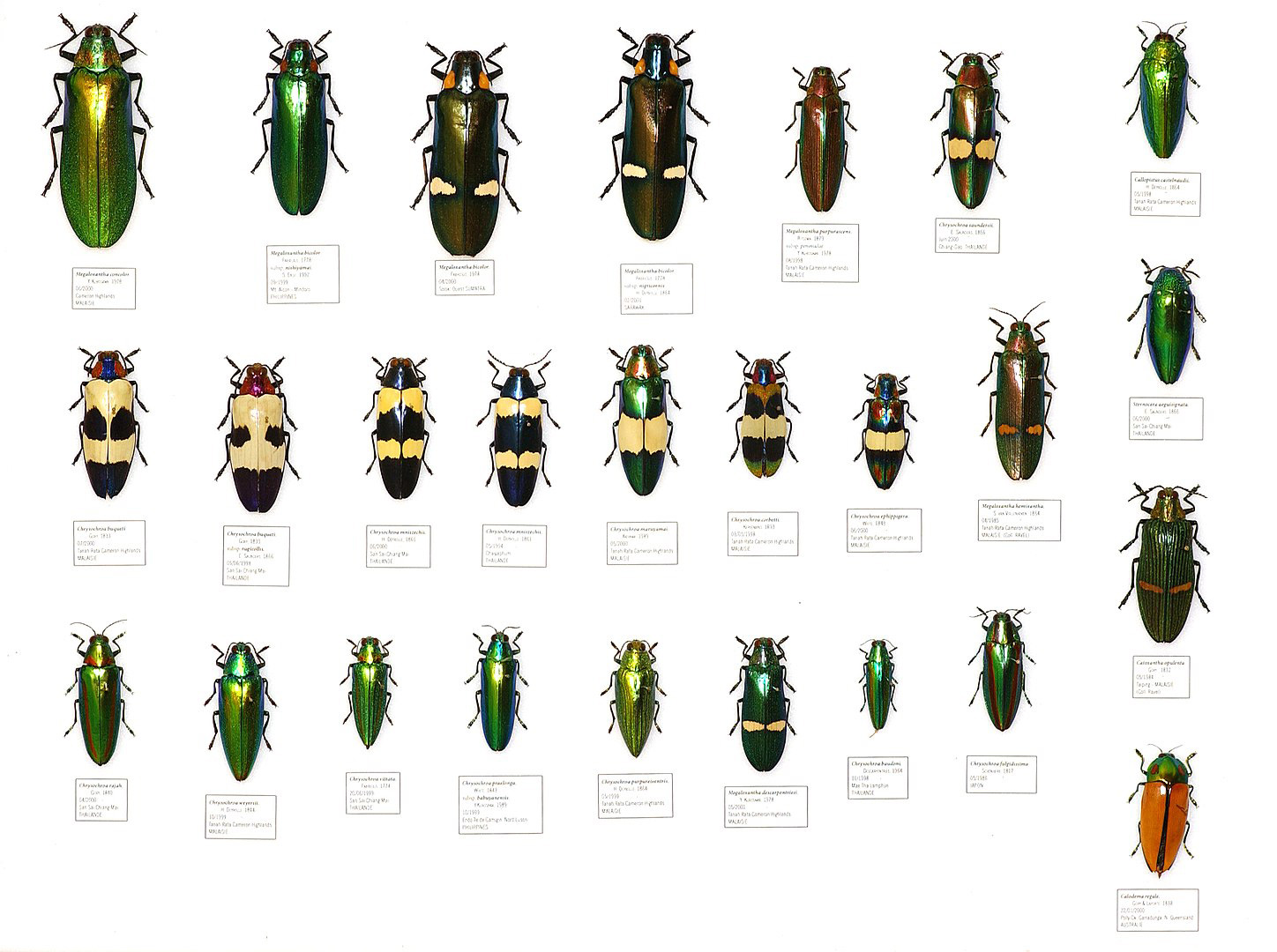
Picture: Some determined examples of jewel beetles
Where does a jewel beetle live?
The jewel beetle lives in farmland, garden, forest, jungle, or woodlands. They may live on a plant or tree that is dying. Some species are attracted to recently burned forests and lay their eggs there. They are known as a tough species, that can thrive in adverse conditions.
What is a jewel beetle’s habitat?
The habitat of the jewel beetle could be any region with abundant plants and trees. That is, they feed and live on the ground as well. They are found on a dying plant or a dying branch of a tree.
Who do jewel beetles live with?
The jewel beetle lives alone most of the time. The jewel beetle habitat may be in the vicinity of other beetles and insects, but they lead a solitary existence until the breeding season. Most beetles spend their whole life in the area or around it.
How long does a jewel beetle live?
The adult jewel beetle lives for three weeks. They may live for a few days or a few weeks. At the pupal stage, the beetle can live for a longer duration even in adverse conditions.
How do they reproduce?
The mating ritual of the jewel beetle is as good as a Roman Gladiator. In certain species, they may fight to the death to win mating rights. Males may fight amongst themselves, or females will fight each other to win mating rights. The strongest one that survives these battles will mate. The mating process usually lasts for a few minutes to several hours. After the mating is over, the female will go to the bark of a tree to lay her eggs. The eggs are laid on the host trees, in the cracks present in the bark of the respective trees.
The life cycle of jewel beetles can be called complete metamorphosis and is divided into four stages, which are egg, larva, pupal, and adult. The larvae of these beetles are known as flat-headed borers, too. Female jewel beetles will lay 20-30 eggs on host trees, usually in the tiny crevice of the bark or under a shoot or a stem. Beetle larvae then grow into a worm-like appearance and are voracious eaters. As they begin to grow, they will discard their outer covering, which is known as the exoskeleton, to have more room. This process is called molting and can happen seven to ten times before it enters the pupal stage. In the pupal stage, the larvae from the pupa or cocoon and lay dormant in it. This is the most transformative stage for the growth of the beetle. This is the time when the larvae take the shape of the adult beetle. The jewel beetle can take anywhere between days to years to grow into a full-fledged adult. After crossing this stage the jewel beetle attends full adulthood.
What is their conservation status?
The conservation status of the jewel beetle is of the Least Concern. We can find them in many places; however, some subspecies that are considered pests may be exterminated using natural or chemical insecticides, causing severe population loss for them.






